XEM is the native cryptocurrency of blockchain project NEM (New Economy Movement). It powers its Smart Asset System – software that makes it easy for developers to create their own applications.
It’s written in Java programming language and was launched in 2015.
XEM Price
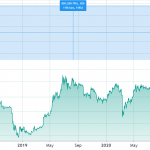
The XEM price recorded an all-time high of $1.87 in January 2018. The cryptocurrency’s all-time low value came in September 2015, when one XEM was priced at $0.00008482.
XEM has a total supply of almost 9 billion tokens, although its maximum supply is unknown.
The tokens were distributed to 1,500 initial stakeholders and multi-signature secured fund wallets for the cost of operating the network. People could sign up to get their stake for free, after which users had to pay in either NXT (an open-source cryptocurrency) or BTC (bitcoin) to get their share of XEM tokens. Initial participants received 4 million XEM tokens each.
XEM’s price has been fairly stable outside of two big moves higher and then lower. Initial interest in the currency perked up in April 2017, when the price went from $0.0239 to its all-time high. A sharp decline followed after that, with the price falling to $0.09 by September 2018. Momentum picked up again in September 2020 as the XEM hit $0.16 and pushed to $0.77 in early March 2021. Since then, its value has fallen back to the $0.09 range.
XEM’s two price peaks coincided with bitcoin’s bull runs, when other cryptocurrencies also rose. Apart from those bullish periods, XEM usually trades between $0.09 and $0.10.
How Does NEM Work?
In the quest to solve energy requirements for consensus algorithms, NEM introduced “proof-of-importance,” or POI. This is a type of agreement mechanism for network participants (called nodes) that involves selecting block validators based on a person’s score. The score is based on factors such as how much value a person has transacted over the past 30-day period in NEM and how frequently a person has traded during that time.
The idea behind POI is it rewards active users on the network, as opposed to the more popular proof-of-stake option, which favors those with the highest staked amount of assets.
The noteworthy feature of NEM is the Eigentrust++ algorithm, which serves as a reputation system for all network nodes. All nodes in the network validate information sent by other nodes. If the information they receive is correct, the reputation of the node that sent the correct information is elevated. Dishonest nodes have their reputations marked down and are eventually removed from the network.
Beyond that, NEM launched Symbol, a next-generation proof-of-stake blockchain, in March 2021. The main feature of Symbol is the creation of tokenized assets.
Key Events and Management
The concept for NEM came from a pseudonymous developer called “Utopianfuture” in 2014. A year later, the protocol was officially launched.
As of October 2021, NEM’s development and promotion occur under the NEM Group banner. The project has no record of raising money from investors, founders or venture capitalists.
The NEM network underwent a fork in August 2017 to lower transaction fees.
The NEM’s Symbol blockchain is interoperable with any public or private network, including layer 2 networks.
In January 2018, Japan-based exchange Coincheck announced more than $534 million worth of XEM tokens had been stolen by hackers – a larger sum than was stolen during the infamous Mt Gox hack. Two months later, NEM called off its search for the hackers and compensated each victim $0.83 for every XEM token he or she lost as a result of the breach.