QTUM is the native cryptocurrency of Qtum, which is a blockchain technology designed to combine the smart contract element of the Ethereum blockchain with the stable blockchain characteristics of Bitcoin and use the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism to verify ownership. Using QTUM, developers can create and deploy their own native decentralized applications (dapps) that get the security benefits of Bitcoin’s blockchain infrastructure.
QTUM Price
QTUM has a total supply of 107.8 million tokens, although its circulating supply is slightly less than that.
The initial QTUM supply consisted of 100 million tokens, which were released during the token’s launch. The supply increases over time because of new blocks adding four new QTUM tokens into circulation as a reward for network validators (people who help verify new transaction data that’s added to the blockchain). The block rewards halve every four years and are expected to reach zero by 2045.
The initial supply was distributed as follows:
- 51% was sold through an initial coin offering (ICO).
- 8% was sold privately.
- The team kept 12% with a four-year lockup period.
- The remaining 29% was put in the hands of the nonprofit Qtum Foundation to be used for promotion, academic research and business development.
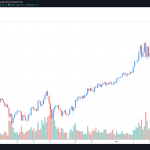
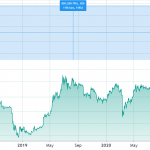
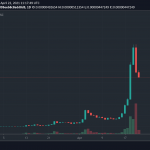
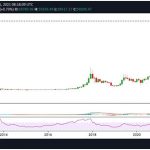
QTUM hit its all-time high of $100.22 in January 2018 and its all-time low of $0.783142 in March 2020.
After the all-time high, the QTUM price began to slide as the broader crypto market retreated, resulting in a price of $4.49 by August 2018. It then continued a further slow decline to the all-time low before picking up some upward momentum in late December 2020.
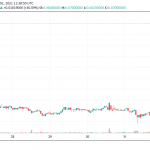
In May 2021, QTUM surpassed $25 again but retraced to $7.5 in the following weeks. The token’s price has remained volatile since then as the prices of other cryptocurrencies have been.
How Does Qtum Work?
Qtum borrows the “unspent transaction output” (UTXO) model from Bitcoin – the system for tracking account balances – and smart contract functionality from Ethereum. It also uses a virtual machine (called x86) like Ethereum does – a computer environment where network participants called nodes can execute smart contracts. The combination of Bitcoin’s transaction model and Ethereum’s smart contracts is possible because of QTUM’s Account Abstraction layer. That tool essentially acts as a bridge between the two technologies.
Additionally, Qtum uses a decentralized governance protocol to let community members vote on things like block sizes and base gas fees without requiring a network hard fork.
Developers can deploy Ethereum dapps on Qtum with ease. As a blockchain, Qtum caters to businesses and developers and it can operate with the systems of external partners.
Key Events and Management
Qtum was founded in 2016 by Chinese blockchain expert Patrick Dai, software developer Neil Mahi of Singapore and Jordan Earls, a web developer from the U.S. All three were still on board with Qtum as of November 2021.
The project secured $1 million during a January 2017 seed fundraising round. Its initial coin offering in March 2017 raised $15.6 million, and Qtum added another $400,000 in funding in December 2018 with a grant.
In 2019, Qtum had a hard fork to Qtum 2.0. The platform upgraded its consensus mechanism and added new features, such as offline staking, chain-cloud integration and confidential assets.