Dai is a stablecoin whose value is pegged to the U.S. dollar, which means it is shielded from the wild swings in prices that are typically associated with a cryptocurrency.
Users generate dai by depositing ether, which is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain, as collateral into Maker Vaults, enabling dai to be minted and entered into circulation. It essentially works like a loan. Users lock up their ether (deposit it into a smart contract) and receive DAI in return. Borrowers can withdraw their locked ether only after they have repaid the amount of dai plus a small interest fee.
The Maker Protocol is the set of smart contracts that make it possible to generate dai, which is held in digital wallets and supported on Ethereum and other blockchains. Smart contracts are self-executing computer programs that automatically complete functions when certain conditions trigger them.
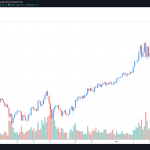
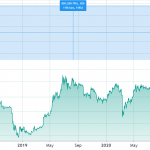
Dai’s Price
Dai was launched in December 2017, almost three years after its governing decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) called MakerDao was created (see below).
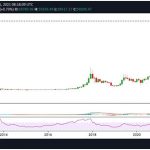
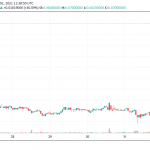
Because the cryptocurrency is pegged to the dollar, dai’s price typically remains around the $1 mark. However, there have been times when its price has shifted away from that level. That usually happens when supply and demand for the stablecoin changes. When supply is high but demand is low, dai’s price tends to hover beneath $1, and vice versa.
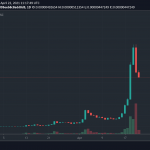
Dai hit an all-time high of $1.14 in September 2020, and an all-time low of $0.8935 in June 2021.
Dai doesn’t have a maximum supply, as it is issued on demand by those who provide the necessary collateral. Dai has a burning mechanism that can be triggered by users who are in debt when they repay the principal of their loan value. However, interest payments – also paid in dai – will recirculate onto the open market.
The stablecoin can be issued only when users submit the proper collateral at the indicated collateralization rate.
How Does Dai Work?
Unlike other stablecoins such as tether (USDT), USD coin (USDC) and binance USD (BUSD), dai is truly decentralized and maintained by MakerDAO.
MakerDAO is an open-source project on the Ethereum blockchain that was created in 2014. People who hold its governance crypto token, MKR, manage the Maker Protocol and the financial risks of dai.
Dai resides on the Ethereum blockchain. It doesn’t have a native consensus algorithm or any specific features other than the ones provided by Ethereum itself.
With dai, users can use the asset’s stability to lend, borrow and invest in various applications, protocols, services and products. It is also a currency to trade against crypto assets, as some exchanges have implemented dai as a base trading option along with other stablecoins.
The creation of dai occurs when a user borrows against their locked collateral – usually 150% of the loaned amount is required upfront as collateral. For example, if you wished to mint $1,000 worth of dai, you would need to deposit $1,500 worth of ether. The amount of borrowed dai will need to be repaid within a certain period or you will automatically lose the collateral.
To maintain its peg to the U.S. dollar, dai relies on a “target rate feedback mechanism,” or TRFM. If the value drops below $1, the TRFM increases to move the price back to the original peg. Such a development allows dai holders to realize a profit and demand for the stablecoin to increase. The process of adjusting the price occurs in a decentralized manner through a software protocol governed by MakerDAO.
Creating dai doesn’t require express permission from anyone, as the protocol is accessible to everyone. Dai and the MakerDAO use an oracle system to collate price data from various external price feeds. Any price feed update is written to the Ethereum blockchain through smart contracts that are owned and deployed by feed operators.
Key Events And Management
MakerDAO, the company responsible for the dai stablecoin, was founded in 2014 by Danish entreprenuer Rune Christensen, who was still the project’s CEO as of November 2021.
The project has received $54.5 million across seven fundraising rounds that have included such notable investors as Bloccelerate, Paradigm Capital Management, Dragonfly Capital Partners, Placeholder, Iconium, Andreessen Horowitz, Walden Bridge Capital, Scanate, 1confirmation and Polychain Capital.