On November 21, researchers from Hungary and Institute for Computer Science and Control published a critical examination of the Lightning Network, the protocol intended to amend BTC’s scalability issues. The researchers’ simulation findings indicate the Lightning Network is “economically irrational for the majority of the large routing nodes who currently hold the network together.”
Also Read: Report: Lightning Network Still Way off Being Ready for Commercial Use
Current Lightning Network Routing Is Not Economically Viable
Many BTC supporters have long believed that the Lightning Network (LN) will be a solution to the Bitcoin blockchain’s scaling problems. Since then the LN protocol has yet to live up to the promises and the network has been plagued with issues. For instance, during the last week of October, one user lost 4 BTC after force-closing an LN channel using an older invalid state. In June, a bug was discovered by developers that allowed LN-based BTC to be spent that was not officially backed by legitimate BTC reserves. LN has been heralded by crypto proponents even though it has been heavily criticized for UX unfriendliness, centralization, and routing issues. Now another study details that the LN project is “economically irrational” while the network also has problems with privacy. The paper’s authors Ferenc Beres, Istvan Seres, and Andras Benczur work at the Institute for Computer Science and Control (SZTAKI) in Hungary alongside Eötvös Loránd and Szechenyi University.

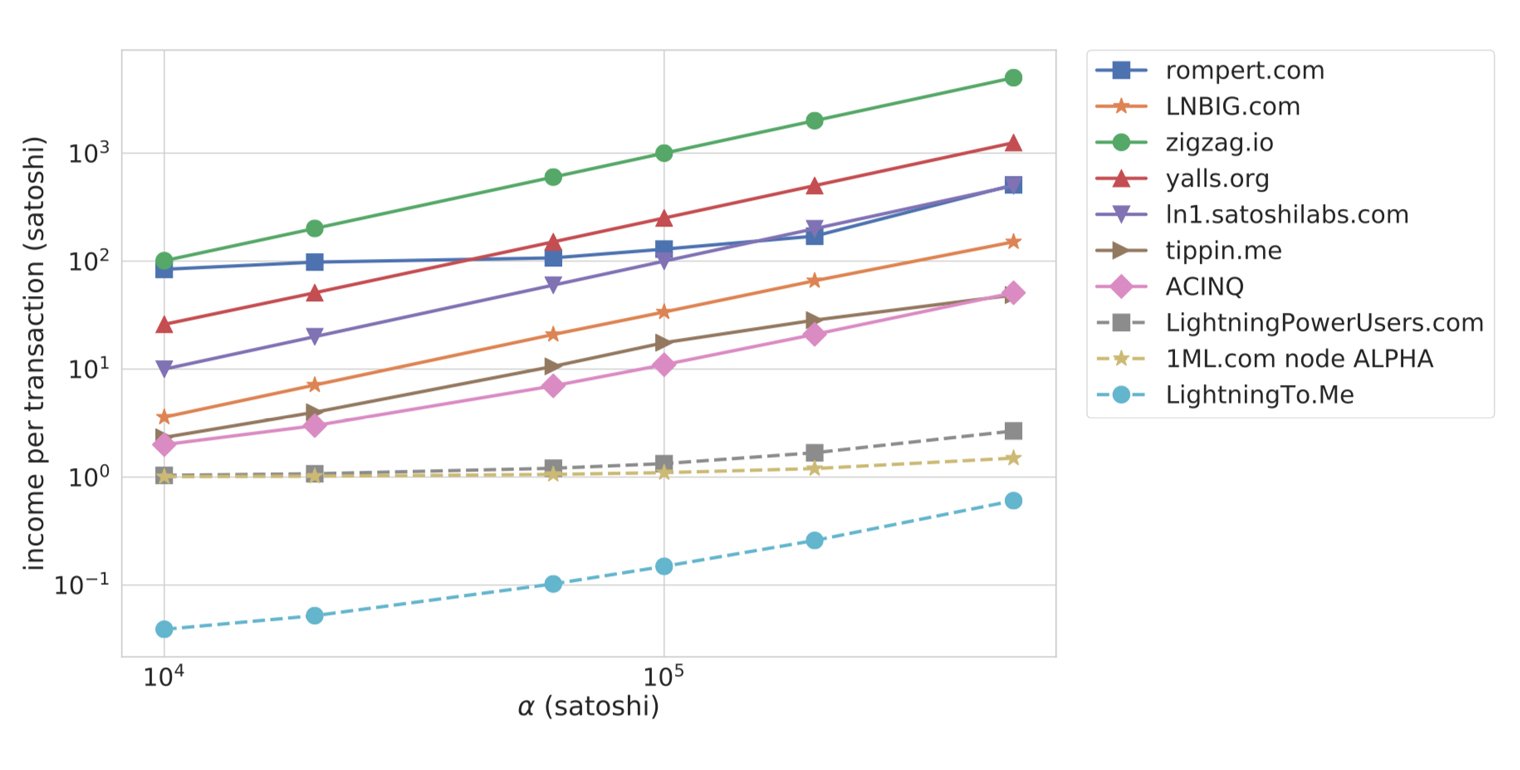
The researchers used a simulator that relies only on publicly available data of the LN framework such as capacity and network structure. The simulation also “generates transactions under assumptions” that the researchers attempted to validate based on information stemming from “LN node owners.” The findings estimate that data deriving from transaction fees shows the LN infrastructure is “economically irrational.”
“Either traffic or transaction fees must increase by orders of magnitude to make payment routing economically viable,” the Hungarian researchers’ paper notes. “We give worst-case estimates for the potential fee increase by assuming strong price competition among the routers. We also estimate how current channel structures and pricing policies respond to a potential increase in traffic and show examples of nodes who are estimated to operate with economically feasible revenue.”
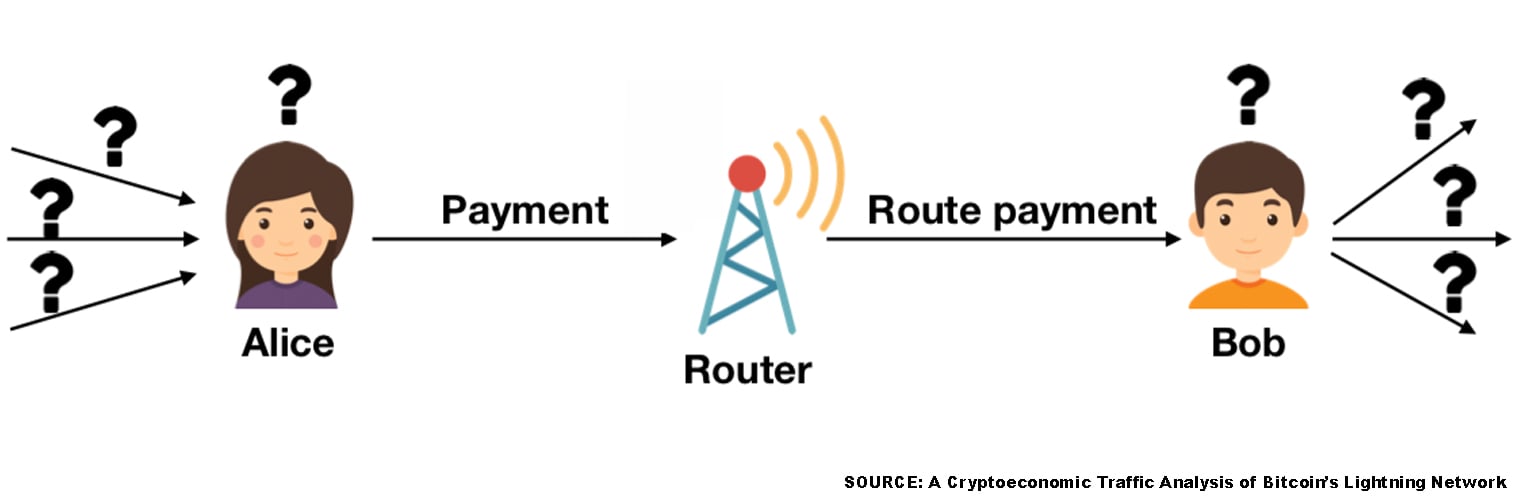
Privacy Shortcomings of Lightning Network Operations
The 21-page study also highlights there are privacy implications that are tethered to using the LN system. “Our second set of findings considers privacy — Even if transactions are onion routed, strong statistical evidence on payment source and destination can be inferred, as many transaction paths only consist of a single intermediary by the side effect of LN’s small-world nature,” the research paper emphasizes. “Based on our simulation experiments, we quantitatively characterize the privacy shortcomings of current LN operation, and propose a method to inject additional hops in routing paths to demonstrate how privacy can be strengthened with very little additional transactional cost.” The researchers have also published the team’s simulator on Github so others can review the study’s process.
The study concludes that the LN simulator provided two key insights. The first and foremost is that a majority of the participation of LN-based router nodes is “economically irrational with the present fee structure.” However, increased overall traffic volume over the network provides possible signs of sustainability. “By contrast, at the present level of usage, if routers start acting rationally, payment fees will rise significantly, which might harm one of LN’s core value propositions, namely, negligible fees,” the paper highlights. Lastly, the topological properties of the current LN framework make “a considerable fraction of payments easily de-anonymizable.”
The proposed solution that the LN provides has been controversial since BTC’s transaction congestion and rising fees. More recently a few Lightning Network proponents have been cheering for higher network fees and those who hope forcefully pushing for LN adoption will be key to the network’s growth. To many skeptics, the current lack of growth, in-depth research papers like the one from Hungary, and seething critiques from business owners suggest that staunch supporters may wish to temper their expectations for the Lightning Network.
If you want to read the researchers’ paper in its entirety you can check it out here.
What do you think about the latest research paper that simulated the Lightning Network? Do you think LN will evolve enough to help support scaling in the future? Or do you agree with the researchers that the LN solution is economically irrational? Let us know in the comments section below.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. It is not an offer or solicitation of an offer to buy or sell, or as a recommendation, endorsement, or sponsorship of any products, services, or companies. Neither the company nor the author is responsible, directly or indirectly, for any damage or loss caused or alleged to be caused by or in connection with the use of or reliance on any content, goods or services mentioned in this article.
Image credits: Shutterstock and the research paper: “A Cryptoeconomic Traffic Analysis of Bitcoin’s Lightning Network.”
Did you know you can buy and sell BCH privately using our noncustodial, peer-to-peer Local Bitcoin Cash trading platform? The local.Bitcoin.com marketplace has thousands of participants from all around the world trading BCH right now. And if you need a bitcoin wallet to securely store your coins, you can download one from us here.
The post Another Research Paper Finds Flaws With the Lightning Network appeared first on Bitcoin News.