
By Jamie Redman,
Back in June MIT Media Lab tested certification authentication using the Bitcoin blockchain. After working on research and development for over a year, the school organization has released an open standard for digital academic certificates called Blockcerts.
Blockcerts Enables Immutable Certification for Anyone
![]() Blockcerts is a MIT Media Lab project utilizing the Bitcoin blockchain for digital notarization. Developers said the platform also allows a decentralized credentialing system. The open source application can be used for “academic, professional, and workforce credentialing.” Blockcerts maintains its foundations as an open software application that allows any individual to take control of their credentials with an immutable method.
Blockcerts is a MIT Media Lab project utilizing the Bitcoin blockchain for digital notarization. Developers said the platform also allows a decentralized credentialing system. The open source application can be used for “academic, professional, and workforce credentialing.” Blockcerts maintains its foundations as an open software application that allows any individual to take control of their credentials with an immutable method.
By putting its application on the Bitcoin blockchain, the project builds a new trust infrastructure. Bitcoin’s protocol removes the dependence on third party arbitration which is impermanent and filled with complication. MIT Media Lab explained the Bitcoin blockchain replaces centralized entities with a “permanent and tamper-proof infrastructure of trust.”
Moreover, the digital ledger is fully transparent, and data can be shared among the public for verification purposes. This gives individuals their own personal notary, and the ability to control their official records. Blockcerts website explains:
Blockcerts is the open standard for blockchain certificates.— Build apps that create, issue, view, and verify blockchain-based certificates within academic credentialing, professional certifications, and workforce development.
Blockchain Technology Could Replicate Historical Methods of Certification
 The research team: Juliana Nazaré, J.Philipp Schmidt, and Kim Hamilton Duffy had written various papers on the subject leading to the launch. Schmidt’s paper proposed the technology could replicate how certification took place in the past. In historical times “journeymen carpenters carried around their books of stamps and references,” explained Schmidt. With distributed ledger technology available to anyone, people can leverage the Bitcoin blockchain for record keeping.
The research team: Juliana Nazaré, J.Philipp Schmidt, and Kim Hamilton Duffy had written various papers on the subject leading to the launch. Schmidt’s paper proposed the technology could replicate how certification took place in the past. In historical times “journeymen carpenters carried around their books of stamps and references,” explained Schmidt. With distributed ledger technology available to anyone, people can leverage the Bitcoin blockchain for record keeping.
“Using the blockchain and strong cryptography, it is now possible to create a certification infrastructure that puts us in control of the full record of our achievements and accomplishments. It will allow us to share a digital degree with an employer while giving the employer complete trust that the degree was in fact issued to the person presenting it,” stated Schmidt.
The MIT Media Lab project has already deployed a few instances of blockchain-based digital certificate verification. In October of 2015, the group issued certificates to Media Lab alumni who attended the Lab’s 30th anniversary. The organization Learning Machine also issued HR certificates to employees. MIT’s Global Entrepreneurship Bootcamp workshop in Seoul, South Korea in March 2016 published digital verification using the system. Lastly, Laboratorio para la Ciudad issued digital certificates to workshop participants in Mexico City in September 2015.
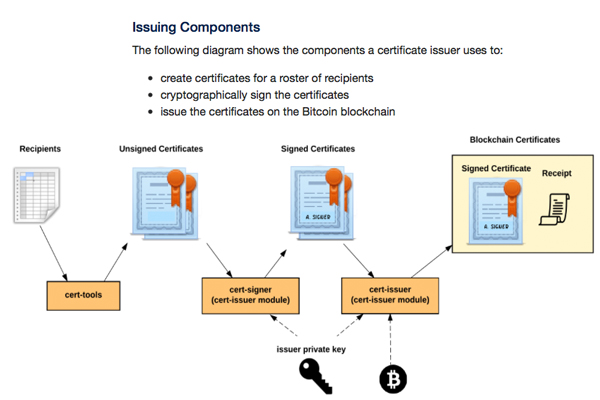
A Distributed Record That Could Help People Continue Progressing Academically, Within a Workforce Environment
The MIT Media Lab developers are quite pleased with the project. This certification process shows the importance of a distributed ledger with immutable permanence. Blockchain certification using Blockcerts is tamper-proof and cannot be updated or edited. However, certification issuers can revoke certain records “by spending the revocation address that they generated for a particular recipient.”
The new process shows a well-researched and developed application that brings a different element to the Bitcoin landscape. The idea of notarization using the Bitcoin blockchain has been known for quite some time, but MIT Media Lab put the idea to work. By building a system that includes step-by-step instructions that are open to anyone, more employers and universities may try the new certification process. The protocol could prevent significant transcript errors as the organization explains stating:
“When certification systems are not working well, the consequences can be more than just inefficient, such as the cumbersome and expensive process of requesting a university transcript: they can be disastrous, such as when a refugee is unable to provide a certificate of completed study and is therefore prevented from continuing her education. Digital systems could help in both of these situations.
